Mechanical pocket watches have been a symbol of elegance and sophistication for centuries. These intricate timepieces have captivated the hearts of watch enthusiasts and collectors alike with their precise movements and timeless designs. While many may appreciate the aesthetic appeal of a mechanical pocket watch, few truly understand the science and engineering behind its movements. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of mechanical pocket watch movements and explore the intricate mechanisms that make these timepieces tick. From the earliest origins of pocket watch movements to the modern advancements in technology, we will take a comprehensive look at the history, evolution, and inner workings of these mechanical marvels. Whether you are a watch enthusiast looking to expand your knowledge or simply curious about the science behind these timeless timepieces, join us as we uncover the secrets and complexities of mechanical pocket watch movements.

Precision mechanics: the heart of pocket watches.
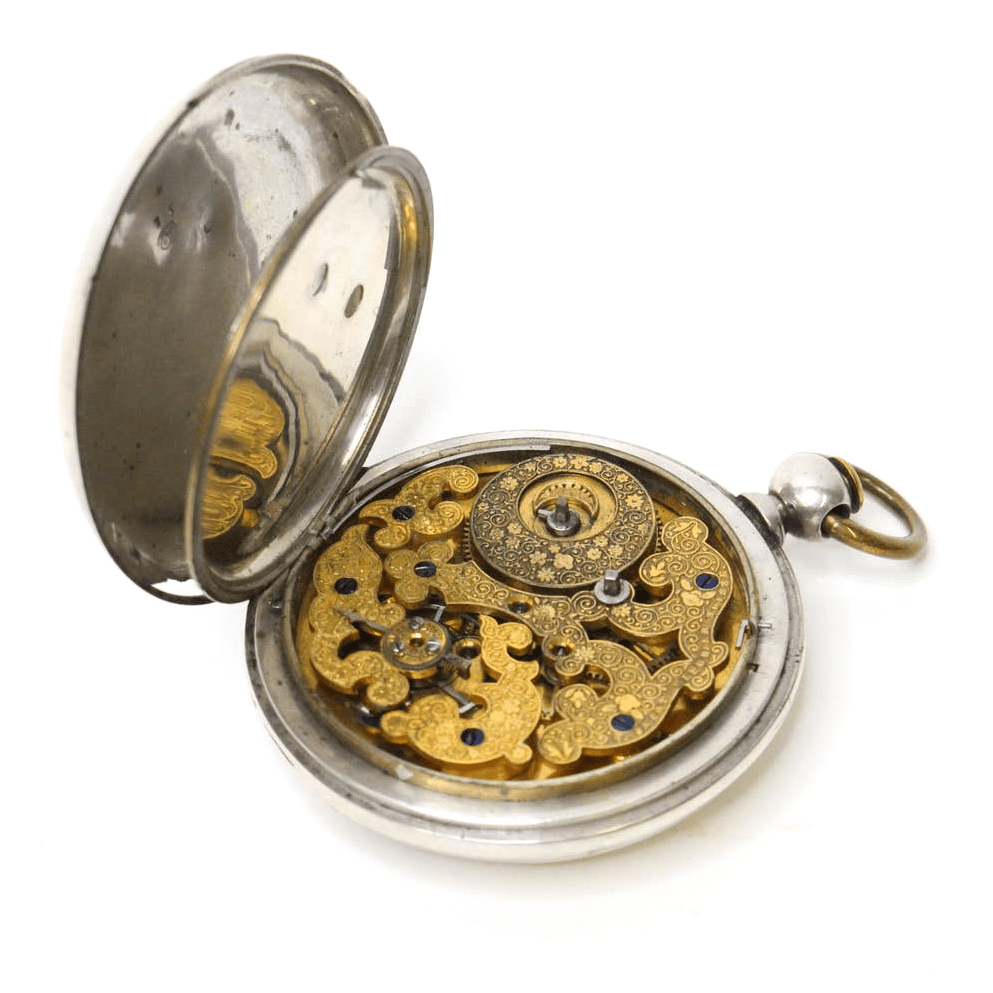
A fundamental aspect that sets mechanical pocket watches apart from their electronic counterparts is the intricate precision mechanics that power their movements. These timepieces have a captivating complexity, with a network of gears, springs, and other mechanical components meticulously calibrated to ensure accurate timekeeping. Each individual part plays a critical role in the overall functioning of the watch, from the mainspring that provides the initial energy, to the escapement mechanism that regulates the release of that energy in a controlled manner. The precise interaction between these components creates a symphony of mechanical harmony, resulting in the smooth and precise movement of the watch’s hands. This intricate craftsmanship and attention to detail exemplify the mastery of precision mechanics that lies at the heart of mechanical pocket watches.
The intricate gears and springs.
The mechanical pocket watch movements are a testament to the intricate craftsmanship and precision engineering that goes into creating these timepieces. Within the inner workings of a mechanical pocket watch, a symphony of gears and springs work in perfect harmony to ensure accurate timekeeping. The gears, meticulously cut and shaped to precise specifications, transmit the energy from the mainspring throughout the watch movement, allowing for the smooth and precise rotation of the hands. These gears are carefully calibrated to maintain the proper ratio, ensuring that each rotation accurately corresponds to the passage of time. The springs, such as the balance spring and the hairspring, provide the necessary tension and oscillation to regulate the movement and ensure its accuracy. The delicate interplay of these gears and springs is a testament to the intricate artistry and engineering that lies within the heart of a mechanical pocket watch.
How power is transferred.
The transfer of power within mechanical pocket watch movements is a fascinating process that relies on the precise coordination of various components. At the heart of this transfer is the mainspring, which stores potential energy when wound and gradually releases it over time. This stored energy is transferred to the escapement mechanism, which consists of a balance wheel and an escapement wheel. As the mainspring unwinds, it exerts force on the escapement wheel, causing it to rotate in small increments. The escapement wheel, in turn, interacts with the balance wheel, creating a back-and-forth motion that regulates the movement of the watch’s hands. This transfer of power is achieved through the careful alignment and interaction of these components, ensuring the accurate and consistent measurement of time. Mastering the art of power transfer in mechanical pocket watch movements requires meticulous engineering and a deep understanding of the delicate interplay between each component.
The role of escapement mechanisms.
The role of escapement mechanisms in mechanical pocket watch movements is critical to their accurate timekeeping. The escapement serves as a control mechanism that regulates the release of energy from the mainspring, allowing the watch to maintain a consistent pace. It achieves this by intermittently engaging and disengaging with the escape wheel, controlling the rotation of the balance wheel. The escapement effectively transforms the continuous energy flow from the mainspring into a precise, evenly spaced oscillation of the balance wheel. This rhythmic motion, in turn, imparts a measured progression to the watch’s hands, ensuring reliable timekeeping. The intricate design and precise craftsmanship of escapement mechanisms play a key role in the overall functionality and performance of mechanical pocket watches.
Understanding the balance wheel.
The balance wheel is a crucial component of mechanical pocket watch movements, contributing to their accuracy and timekeeping capabilities. It consists of a circular wheel with weighted arms or spokes that oscillate back and forth, driven by the energy released from the mainspring through the escapement mechanism. The balance wheel’s oscillations are carefully regulated by the hairspring, a coiled spring that acts as a restoring force, ensuring that the wheel swings back and forth at a consistent rate. By controlling the speed and duration of these oscillations, the balance wheel determines the watch’s timing and accuracy. Fine-tuning the balance wheel’s size, weight, and spring tension is a delicate process, requiring skilled craftsmanship, as even minor adjustments can significantly impact the watch’s performance. Understanding the intricacies of the balance wheel is essential in appreciating the meticulous craftsmanship and engineering that goes into mechanical pocket watch movements.
The importance of lubrication.
Proper lubrication is an essential aspect of maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of mechanical pocket watch movements. The intricate mechanisms within these timepieces rely on precise and smooth movements to accurately measure time. Lubricants, specifically designed for horological applications, minimize friction between the various components, reducing wear and tear. This not only ensures the smooth operation of the watch, but also prevents excessive wear on delicate parts, such as the pivots and gears. By regularly lubricating the movement, watchmakers can mitigate the effects of friction, minimize the risk of damage, and preserve the functionality of these intricate timekeeping devices.
Different types of movements.
There are several different types of movements commonly found in mechanical pocket watches, each offering its own unique characteristics and functions. One common movement is the manual wind movement, where the watch is powered by manually winding the crown. This traditional movement requires regular winding to keep the watch running. Another type is the automatic movement, which uses the natural motion of the wearer’s wrist to wind the watch through a rotor mechanism. This eliminates the need for manual winding, making it convenient for those who prefer a more effortless timekeeping experience. Additionally, there are also quartz movements, which utilize a battery to power the watch and provide highly accurate timekeeping. These movements are known for their reliability and precision. Each type of movement offers its own advantages, catering to the preferences and needs of watch enthusiasts.
Traditional vs modern manufacturing processes.
In the realm of manufacturing processes, there has been a significant shift from traditional methods to modern techniques. Traditional manufacturing processes often involve manual labor, where skilled craftsmen meticulously create products by hand. These methods are known for their attention to detail and craftsmanship, but they can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. On the other hand, modern manufacturing processes have embraced automation and technology, allowing for greater efficiency and precision. Computer-controlled machinery and robotic systems have revolutionized production lines, enabling faster production rates and consistent quality. Additionally, modern processes often integrate advanced materials and innovative techniques, resulting in enhanced durability and functionality in the final product. While traditional methods may still hold appeal for those seeking artisanal craftsmanship, modern manufacturing processes offer streamlined production and improved capabilities to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
Maintaining and repairing movements.
With advancements in technology, maintaining and repairing mechanical pocket watch movements has become a specialized skill in the horology industry. Professionals in this field possess a deep understanding of the intricate mechanisms and components that make up these movements. They are well-versed in the art of disassembling, cleaning, and lubricating the delicate gears, springs, and escapements to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, they have the expertise to identify and rectify any issues that may arise, such as worn-out parts or misalignments. By adhering to strict quality standards and utilizing precision tools, these professionals can effectively restore the functionality and longevity of these mechanical wonders, preserving their historical and sentimental value for years to come.
The beauty and complexity within.
The Science Behind Mechanical Pocket Watch Movements delves into the fascinating world of these intricate timekeeping devices, showcasing the beauty and complexity within. Each mechanical pocket watch movement is a testament to precision engineering, with a myriad of finely crafted gears, levers, and springs working in harmony to measure the passing moments. The craftsmanship involved in creating these movements is awe-inspiring, as master watchmakers painstakingly assemble and adjust each component to ensure accurate timekeeping. The intricate patterns and engravings on the movement plates further enhance their visual appeal, showcasing the attention to detail and artistic flair inherent in these timepieces. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, the complexity within these movements is a testament to human ingenuity and the quest for measuring time with unparalleled precision.
In conclusion, the intricate and precise movements of mechanical pocket watches are a testament to the art and science of watchmaking. From the mainspring to the escapement, every component plays a crucial role in keeping time accurately and elegantly. The craftsmanship and engineering behind these movements are truly remarkable and continue to be appreciated by watch enthusiasts and collectors alike. Whether it’s a vintage piece or a modern design, the complexity of mechanical pocket watch movements is a testament to the beauty and ingenuity of human innovation.
FAQ
How do mechanical pocket watch movements work and what differentiates them from other types of watch movements?
Mechanical pocket watch movements operate through a series of gears, springs, and escapements that regulate the passage of time. Unlike quartz movements found in most modern watches, mechanical movements are powered by a mainspring that must be wound manually. The intricate mechanical components in pocket watch movements require skilled craftsmanship to assemble and maintain, making them a traditional and sought-after choice for watch enthusiasts. Additionally, the absence of electronic components in mechanical movements gives them a classic appeal and a unique charm that sets them apart from their more modern counterparts.
What are the key components of a mechanical pocket watch movement and how do they interact to keep time accurately?
The key components of a mechanical pocket watch movement include the mainspring, balance wheel, escapement mechanism, gear train, and hands. The mainspring stores energy, which is transferred through the gear train to the escapement mechanism, controlling the release of energy to the balance wheel. The balance wheel oscillates back and forth, regulating the movement of the gears and hands. The escapement mechanism ensures the precise release of energy from the mainspring, while the gear train balances the speed of the movement. Together, these components work harmoniously to maintain accurate timekeeping in a mechanical pocket watch.
How does the escapement mechanism in a mechanical pocket watch movement regulate the release of energy to ensure consistent timekeeping?
The escapement mechanism in a mechanical pocket watch movement regulates the release of energy by controlling the rotation of the gear train and the movement of the balance wheel. It consists of a pallet fork that interacts with the escape wheel, allowing the gear train to advance in small, precise increments. This action controls the release of energy from the mainspring, ensuring that the balance wheel oscillates at a consistent rate and ultimately regulates the timekeeping of the watch.
What are some common complications found in mechanical pocket watch movements and how do they enhance the functionality of the timepiece?
Common complications in mechanical pocket watch movements include chronograph, moon phase, tourbillon, and perpetual calendar. These complications enhance the functionality of the timepiece by providing additional features beyond basic timekeeping. For example, a chronograph allows for precise timing of events, a moon phase complication tracks lunar cycles, a tourbillon improves accuracy by counteracting the effects of gravity, and a perpetual calendar displays the date, day, month, and leap year information. These complications add complexity and craftsmanship to the watch, making it both functional and aesthetically appealing.
How has the design and engineering of mechanical pocket watch movements evolved over time to improve accuracy and reliability?
The design and engineering of mechanical pocket watch movements have evolved over time through advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and technology. Innovations such as the use of jeweled bearings, precision machining, and improved escapements have greatly enhanced the accuracy and reliability of pocket watches. Additionally, the development of shock-resistant systems, temperature compensation mechanisms, and anti-magnetic materials have further improved the performance of mechanical movements. These continuous improvements have allowed pocket watches to maintain high levels of accuracy and reliability, making them a timeless and enduring timekeeping device.