Since their introduction in the 16th century, pocket watches have been a symbol of prestige and an essential accessory for the well-dressed gentleman. The evolution of the pocket watch was marked by many challenges, technological advancements and a thirst for accuracy. The movements of pocket watches in specific, have undergone a significant transformation due to the evolution of various timekeeping devices. From early attempts at regulating time accuracy to the development of more sophisticated movements, the history of pocket watches has much to say about the progress of timekeeping devices.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the evolution of pocket watch movements from the 16th century to the 20th. We’ll explore early attempts at accuracy through the introduction of the verge escapement in the 17th century, the Swiss lever escapement in the 19th century, and the quest for extreme precision with the development of the chronometer.
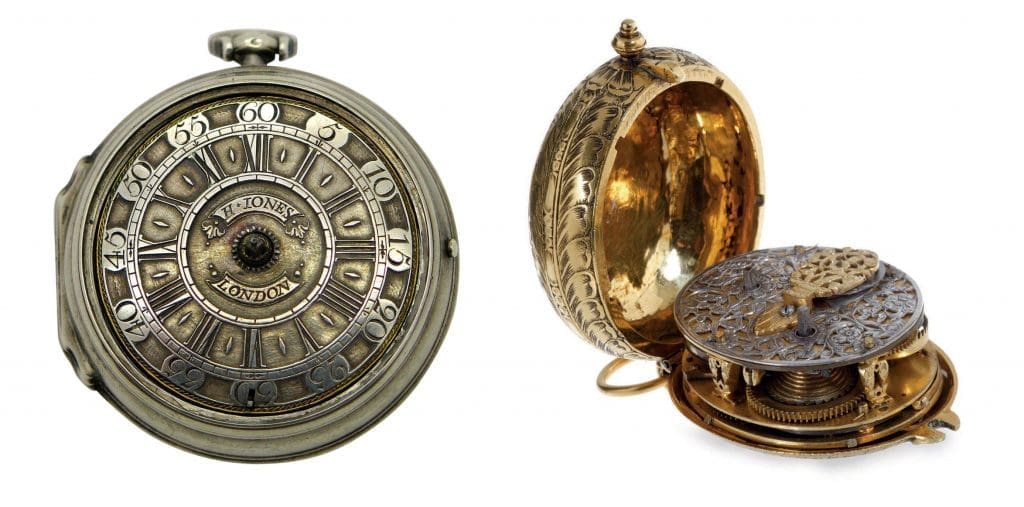

1. The first pocket watch movements were introduced in the 16th century and were made of iron and brass.
The evolution of pocket watch movements is a fascinating study that can be traced back to the 16th century. During this time, the first pocket watch movements were introduced and were primarily made of iron and brass. These early pocket watch movements were quite basic and did not include some of the sophisticated mechanisms that we see in modern-day pocket watches. Over time, watchmakers refined their craft and introduced new improvements to the designs of pocket watch movements. In the 17th and 18th centuries, for instance, the addition of the balance wheel made pocket watches more accurate and precise. The evolution continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, with watchmakers introducing new mechanisms like the lever escapement, which improved accuracy even further. The evolution of pocket watch movements over time is a testament to human ingenuity and technological advancement.
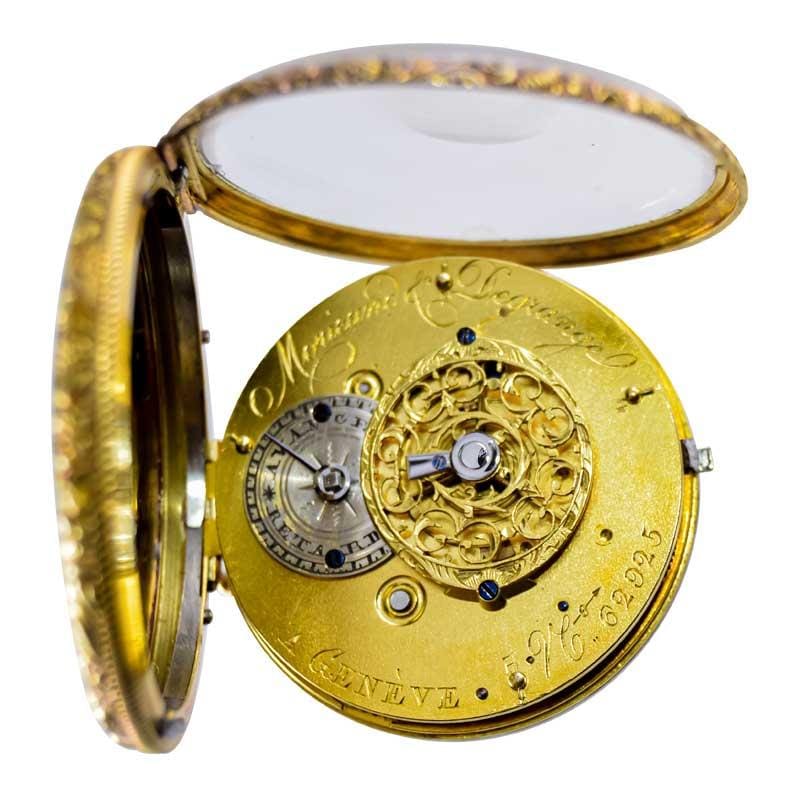

2. In the 17th century, pocket watches began to feature a balance wheel and a hairspring, which improved accuracy.
The evolution of pocket watch movements from 16th century to 20th can be traced through several key developments that transformed the accuracy and mechanics of these timepieces. One such development occurred in the 17th century when pocket watches began featuring a balance wheel and a hairspring. This represented a significant improvement in accuracy over earlier models. Prior to this development, pocket watches relied on a verge escapement system that performed with limited accuracy. The balance wheel and hairspring allowed for more precise timekeeping and increased portability, making pocket watches an even more essential tool for professionals and individuals alike. The introduction of these components further paved the way for the miniature mechanics of pocket watches and helped establish the foundation for the intricate movements that would continue to evolve through to the 20th century.
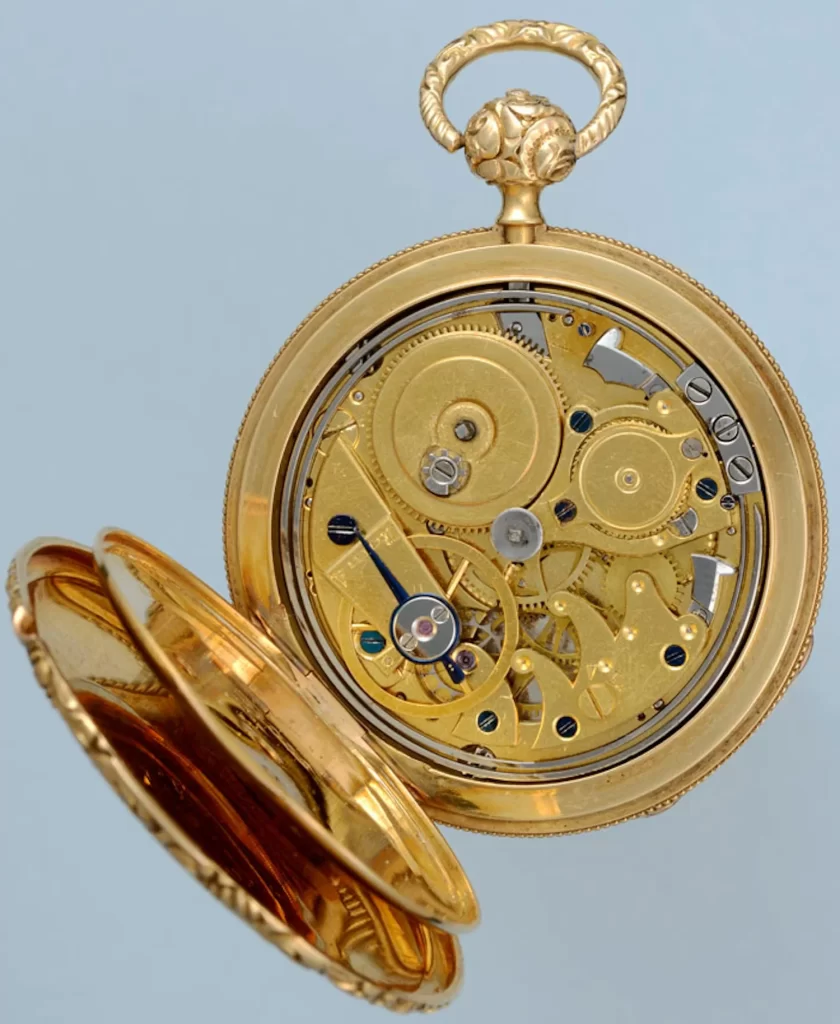

3. The 18th century saw the introduction of the cylinder escapement, which further improved accuracy.
The evolution of pocket watch movements from the 16th century to the 20th century saw significant developments that improved accuracy and functionality. The 18th century proved to be a crucial period in this evolution as the cylinder escapement was introduced, revolutionizing timekeeping accuracy. The cylinder escapement is a type of escapement that uses a cylinder-shaped roller instead of the traditional lever escapement. It enabled pocket watches to keep accurate time for longer periods by reducing friction and wear on the watch’s mechanical components. The cylinder escapement was a key step in the development of modern pocket watch movements that allowed watchmakers to produce more precise and reliable timepieces, making them more widely available to the general public.
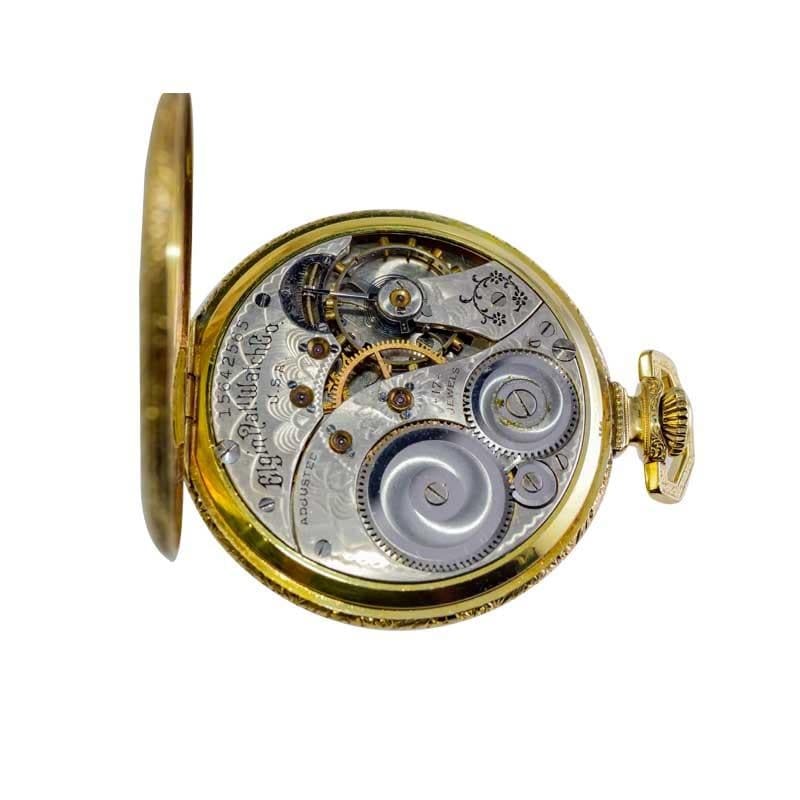

4. In the 19th century, the lever escapement was introduced, which is still used in modern pocket watches.
The 19th century marked a significant milestone in the evolution of pocket watch movements with the introduction of the lever escapement, which is still used in modern pocket watches. Prior to this, older designs such as the verge and fusee movements were widely used. The lever escapement was developed by Thomas Mudge in 1755 and was refined over the years until it became the standard for accuracy and reliability in watchmaking. This new design reduced the friction and enhanced the accuracy of the timepiece. Its primary components included a pallet fork, which engaged with the escapement wheel, which in turn controlled the balance wheel. Even after the introduction of the quartz movement in the 20th century, many pocket watch enthusiasts still prize the classic lever escapement for its historical and traditional value.
5. The 19th century also saw the introduction of the Swiss Anchor Escapement, which was widely adopted.
The pocket watch movements began to evolve rapidly in the 19th century. One of the most significant developments during this time was the introduction of the Swiss Anchor Escapement, which was widely adopted. This advancement was a significant breakthrough for the watch industry, as it paved the way for the creation of much more accurate timepieces. Until then, pocket watches had been known to lose considerable amounts of time, and there was a demand for more accurate watches. The Swiss Anchor Escapement was a significant improvement over the previous cylinder escapement that was used in most pocket watches at that time, and it soon became the standard in the industry. The anchor escapement is still in use today, over 150 years later, and is one of the most important inventions in the history of watchmaking.
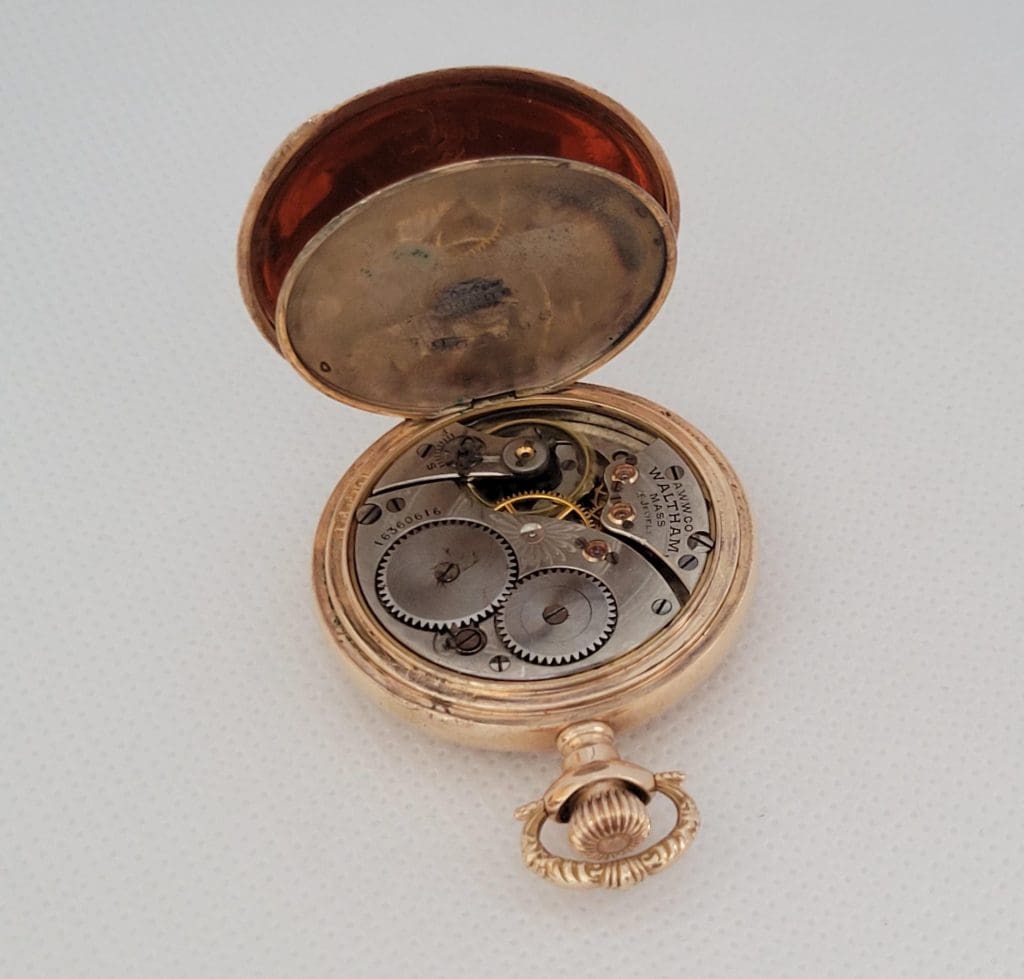

6. In the late 19th century, the jeweled movement was introduced, which used synthetic jewels to reduce friction and improve accuracy.
The late 19th century marked a new era in the evolution of pocket watch movements with the introduction of the jeweled movement. The jeweled movement was a significant shift from earlier pocket watch movements as it used synthetic jewels in place of metal bearings. The primary purpose of these jewels was to reduce friction and improve the accuracy of pocket watches. The use of synthetic jewels in pocket watch movements was a game-changer that significantly improved pocket watch technology. This innovation also paved the way for the development of modern watches that still use synthetic jewels today to reduce friction in their movements. The jeweled movement marked a crucial turning point in the evolution of pocket watch movements, and its legacy lives on in modern-day watchmaking.
7. The early 20th century saw the introduction of the quartz movement, which revolutionized timekeeping.
The early 20th century marked a significant turning point in the evolution of pocket watch movements with the advent of the quartz movement. This innovation was made possible by the discovery of quartz crystal’s piezoelectric property – which means it generates electricity when subjected to mechanical pressure. By leveraging this property, the quartz movement could provide a more accurate means of measuring time compared to previous mechanical movements. Additionally, the quartz movement was also more affordable to produce and hence made pocket watches more accessible to the masses. The adoption of quartz movements had far-reaching implications and revolutionized the field of timekeeping not only in pocket watches but also in other timekeeping devices.
8. The quartz movement was followed by the introduction of the automatic movement, which uses the movement of the wearer’s wrist to wind the watch.
The evolution of pocket watch movements from the 16th century to the 20th century is a fascinating journey, showcasing several engineering marvels. In the mid-20th century, the quartz movement revolutionized the watch industry with its exceptional accuracy and reliability. Following this invention, the automatic movement was introduced, responding to the needs of consumers for a more convenient and low-maintenance option. The automatic movement utilizes the movement of the wearer’s wrist to wind the watch, eliminating the need for a daily winding routine. This innovation made it possible for the watch to run without a battery or a spring-powered manual winding mechanism while ensuring perpetuity of power. Thanks to the automatic movement, wristwatches became a more practical and functional device, eventually taking over the market and making pocket watches a collector’s item.
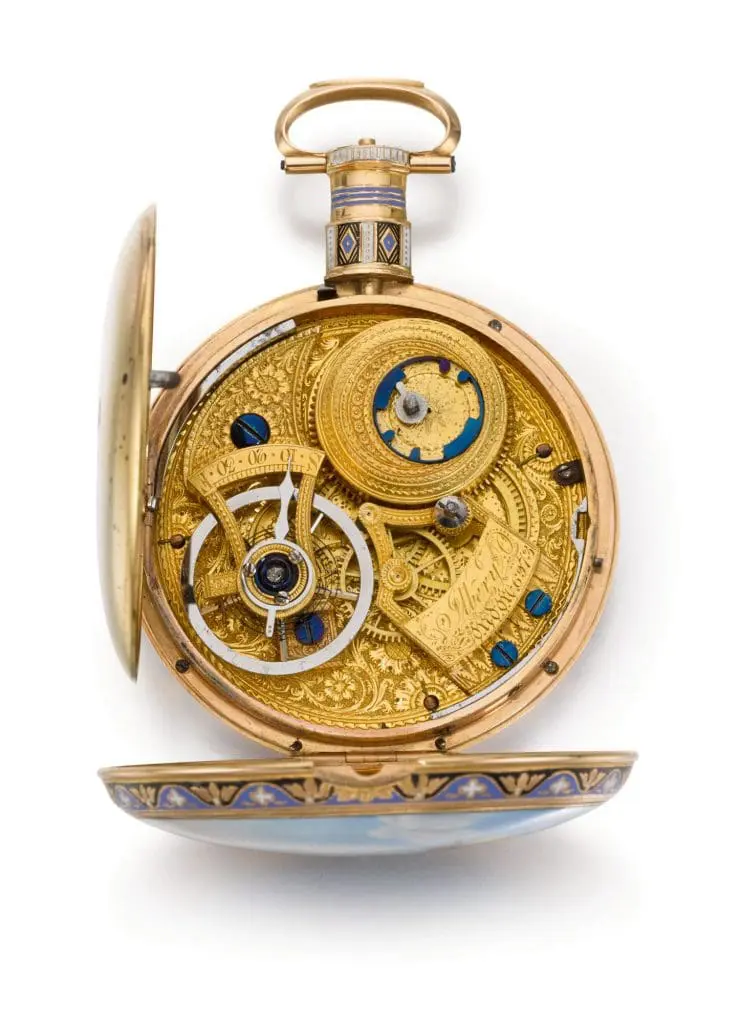

In conclusion, the evolution of pocket watch movements is a fascinating journey spanning centuries. From the earliest verge escapement movements to the complex and precise chronometer movements of the 20th century, the pocket watch has undergone significant changes and technological advancements. The pocket watch has served as a symbol of style, status, and utility throughout history, and its evolution is a testament to human ingenuity and innovation. Even though technology has replaced pocket watches with modern devices, they remain a significant piece of mechanical engineering history and an object of fascination for collectors and enthusiasts alike.